Intellectual Property and Research

SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR DYNAMIC STATE TRANSPOSITION AND PREEMPTIVE EVASION OF SPATIOTEMPORAL CORRELATED ERRORS
A novel hardware architecture that allows quantum processors to physically "dodge" errors. Unlike traditional error correction which reacts to noise after it happens, this system utilizes a dynamic lattice topology to preemptively transpose quantum states into a "safety manifold" before impact. This active evasion protocol preserves coherence without the massive overhead of standard correction cycles.
SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR RESOLVING COSMIC RAY EVENTS IN SUPERCONDUCTING QUANTUM PROCESSORS VIA ADAPTIVE CONTROL SYSTEMS
Describing a hardware-integrated, adaptive control layer, this filing outlines a novel architecture designed to mitigate the impact of correlated environmental noise—such as high-energy ionizing radiation—which currently serves as a critical barrier to the scalability of superconducting quantum architectures. By utilizing high-speed, pre-computed logic structures to perform real-time error signature identification, the proposed system targets autonomous mitigation protocols within the processor’s ultra-short coherence window. This approach aims to bridge the latency gap between complex predictive modeling and physical hardware execution, offering a robust framework toward fault-tolerant quantum computing by ensuring logical circuit integrity in the presence of massive, simultaneous error bursts.
Empirical Tests for a Hedging Framework for the Quantum Binomial Options Pricing Model
The Quantum Binomial Options Pricing Model is a novel approach to pricing derivatives. It serves as a quantum analogue to the classical binomial options pricing model, using concepts from quantum mechanics like the Pauli matrices and Bloch sphere to represent the derivatives market. Through usage of a density matrix and mixed states, the model can potentially price derivatives more accurately. However, at this time there exist no clear formulae and methods for hedging derivatives through this model. This paper numerically tests the performance of the hedging framework corresponding to the model as compared to the classical model using a year of historical S&P 500 data. The simulation reveals that the Quantum Binomial Options Pricing model is, at least in its current state, not viable for usage in actually hedging derivatives. This is due to numerical instabilities, particularly in the Quantum Theta and Quantum Vega, the former of which ends up negative, betraying fundamental financial postulates, and the latter of which is blown out of scale. We hypothesize that these nonsensical values for Quantum Theta and Quantum Vega stem from the single period nature of the model we tested, as well as the isotropic assumption of the operator A. We conclude that the single period Quantum Binomial Options Pricing Model is currently unsuitable for practical applications of hedging and that our findings reveal the necessity of rigorously testing new financial models against benchmark models like the Classical Binomial Options Pricing Model.
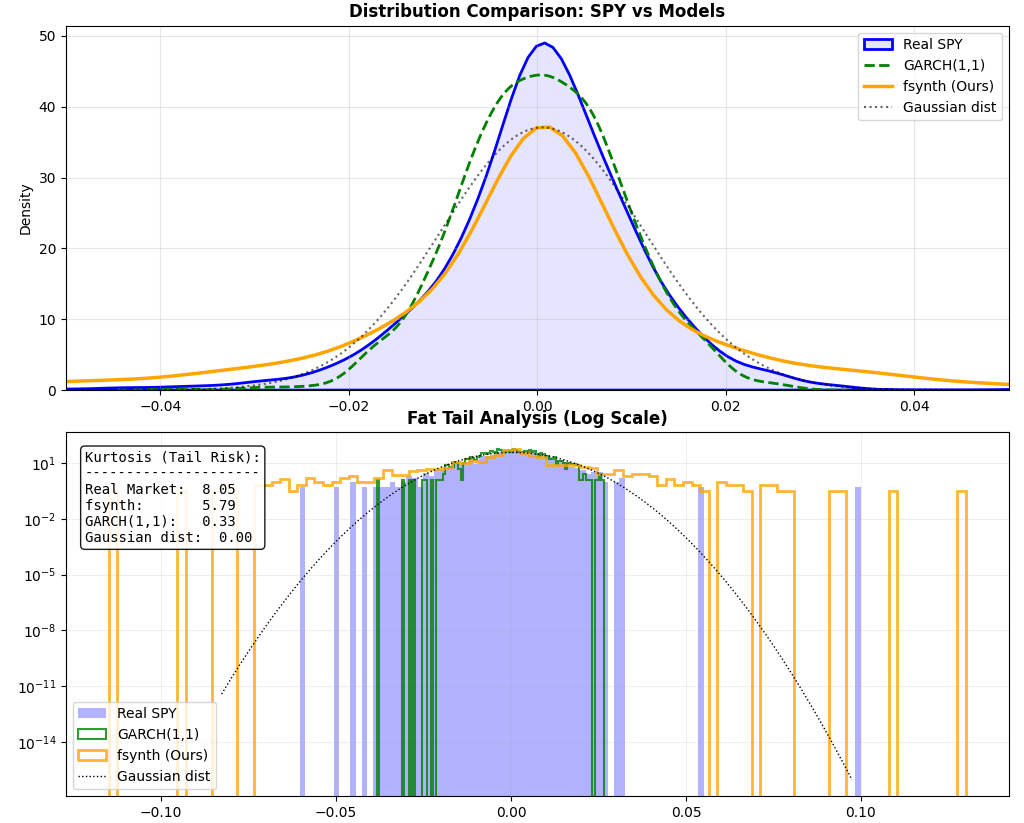
High Fidelity Synthetic Financial Universes Through Regime Switching With Stochastic Volatility and Jump Diffusion
Traditional machine learning models trained on financial market data are known to be highly susceptible to overfitting the past market. Historical data is limited, and models trained only on data from the past will only be able to perform well in financial conditions mimicking the past. To combat this data scarcity, many use mathematical generators of unlimited synthetic data. However, traditional synthetic data generators often rely on Geometric Brownian Motion (GBM), which fails to account for empirical phenomena such as volatility clustering, leverage effects, and ”black swan” jump events. This paper introduces fsynth, a multi-factor synthetic engine that integrates a Heston-based stochastic volatility model with Merton jump diffusion, governed by a hidden Markov regime-switching process. By using macro-regime states alongside company specific ”genes,” the engine generates plausible universes containing both price action and fundamental accounting data. We demonstrate that while the engine can be calibrated to replicate conditions of historical benchmarks, its primary utility lies in its parameterizable nature, allowing for the simulation of arbitrary, ”out-of-sample” stress scenarios.
pip install fsynth

